Oil immersed transformer
Transformer protection- Some typical equipments for protecting a transformer
There are different types of transformers: two-winding or three-coil power transformers, autotransformers, tuning transformers, grounding transformers, rectifying transformers, etc.
It is common practice to provide relay protection by Buchholz for all transformers 0.5 MVA and above. For all small distribution transformers, only the high voltage fuse is used as the primary protection device. For all larger nominal and critical distribution transformers, overcurrent protection together with limited earth fault protection applies.
Below are some transformer faults that commonly happen. We also have transformer protection device to prevent transformers for these faults.
Table of contents:
1. Stresses generated by the supply source-protection of transformer
3. Overload and internal fault of the dry type transformer- transformer protection
4. Errors between turns should be carefully considered
1. Stresses generated by the supply source- protection of transformer
Two types of over voltages may stress and even destroy a transformer:
Lightning overvoltages caused by lightning falling on or near overhead lines supplied to the building where the transformer is to be installed
For example, voltage conversion is caused by opening a circuit breaker or a load breaker.
Depending on the application, protection against these two types of voltages may be necessary and is usually ensured by ZnO surge protectors, preferably connected on the transformer MV bushing.
2. Stress due to load
Transformer overload is always due to an increase in the installation's apparent power demand (kVA). This increase in demand may be the result of an increasing combination of loads or an expansion of the installation itself. The effect of any overload is an increase in the temperature of the oil, and the transformer windings shorten its service life.
The protection of the transformer against overload is accomplished by a dedicated protection commonly referred to as the thermal overload relay. This type of protection simulates the temperature of the transformer winding which is based on current and thermal time constant measurements of the transformer. Some relays can consider the harmonic effect of currents due to non-linear loads such as rectifiers, computers, variable speed transmitters, etc. before emitting collision order and time delay then the transformer is energized again.
In addition, the oil-filled transformer is equipped with a thermostat that controls the oil's temperature.
Dry-type transformers use thermal sensors embedded in the hottest part of the insulation of the windings.
Each of these devices (thermal relay, thermostat, temperature sensor) typically provides two levels of detection:
Low levels are used to generate alerts to notify maintenance personnel,
High level to de-energize the transformer.
Defects inside the oil-filled transformer
In an oil-filled transformer, internal faults can be classified as follows:
The main faults of gas generation are:
Micro arc due to initial fault in coil insulation
Slow degradation of the insulation material
Inter variable short circuit
Errors generate internal overvoltage simultaneously with high current on the line:
Short-circuit to ground phase
Phase short circuit.
These errors can be the result of external lightning or from overvoltage switching.
Depending on the transformer type, there are two types of devices that can detect an oil-filled transformer's internal faults.
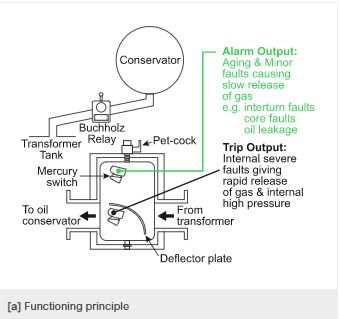
Buchholz is dedicated to transformers equipped with breathing air preservatives (see Figure B16a).
Breathing transformer protected by buchholz
Buchholz was installed on the pipe connecting the transformer tank to the storage machine (see Figure B16b). It retains slow emissions and detects oil backflow due to internal pressure
DGPT (Gas, Pressure and Temperature Detection,see Fig. B18) for integrated transformers (see Fig. B17). This type of transformer is manufactured up to about 10 MVA. DGPT as buchholz detects gas emissions and internal pressure. In addition, it monitors the temperature of the oil.
Fig. B18 – DGPT (Detection of Gas, Pressure and Temperature) protection relay for integral filled transformers
With regard to gas and temperature monitoring, buchholz and DGPT offer two levels of detection:
- Low levels are used to generate alerts to notify maintenance personnel,
- High level to disconnect the switch installed on the primary side of the transformer (circuit breaker or load breaker is associated with a fuse).
In addition, both buchholz and DGPT are suitable for detecting oil leaks.
3. Overload and internal fault of the dry type transformer- transformer protection
(see Fig. B19 and Fig. B20)
Dry-type transformers are protected against overheating due to possible overload downstream with dedicated relay supervised thermal sensors mounted in the windings of the transformer
Internal faults, mainly between loops and ground-to-ground short circuits occur inside a dry-type transformer cleaned with a circuit breaker or fuse installed on the primary side of the transformer. When used, the ground contact of the circuit breaker is arranged in phase-to-phase order and phase to earth for overcurrent protection.
4. Errors between turns should be carefully considered:
They usually produce moderate flow across the line. For example when short-circuiting 5% of the HV coil the transformer current does not exceed 2 In, for the short-circuit affecting 10% of the winding, the current is limited around 3 In.
Fuses are not suitable for the proper removal of such currents
Dry-type transformers are not equipped with additional protective devices such as the DGPT dedicated to internal fault detection.
As a result, internal faults that produce an excessively low current may not be safely released by a fuse. Protection with an overcurrent relay with the right characteristics and settings (e.g. Schneider Electric's VIP relay strip) is preferred).




Nhận xét
Đăng nhận xét